Caring for pets can be great for kids, teaching them responsibility, gentleness, and respect for other living beings.
Have you ever noticed your furry friend scratching more than usual only to find yourself itching a few days later? You’re not imagining things – some dog skin conditions can absolutely transfer to humans! As someone who’s seen this firsthand (my entire family once got scabies when I was younger) I want to share what I’ve learned about these transferable skin problems.
The Uncomfortable Truth: Zoonotic Skin Conditions
Your dog isn’t just your best friend – they’re also a potential carrier of what doctors call “zoonotic diseases.” These are conditions that can pass from animals to humans, and several skin problems fall into this category.
When your pup is rolling around outside, playing at dog parks, or just exploring the neighborhood, they’re picking up all sorts of things. Some of these hitchhikers can end up on your skin too, especially if you’re like me and can’t resist snuggling with your four-legged buddy or letting them sleep in your bed
What’s even more surprising? Your dog doesn’t necessarily need to have symptoms themselves to pass something on to you! They can act as a carrier, bringing home unwelcome guests that find their way to your skin.
5 Common Skin Conditions Dogs Can Transfer to Humans
Let’s look at the most common skin problems that can jump from your pup to you:
1. Ringworm
Despite its name, ringworm isn’t actually a worm at all – it’s a fungal infection. This highly contagious condition causes circular, red, itchy patches on the skin and can cause hair loss in both dogs and humans.
What it looks like in dogs: Circular patches of hair loss, redness, and crusty skin.
What it looks like in humans: Ring-shaped red rash that might be itchy or scaly.
How it transfers: Direct contact with an infected dog’s skin or hair, or contact with contaminated items like bedding, brushes, or furniture. The fungus can live on surfaces for months!
Treatment: Antifungal medications for both you and your dog. You’ll need to treat your pet, yourself, and thoroughly clean your home to eliminate the fungus.
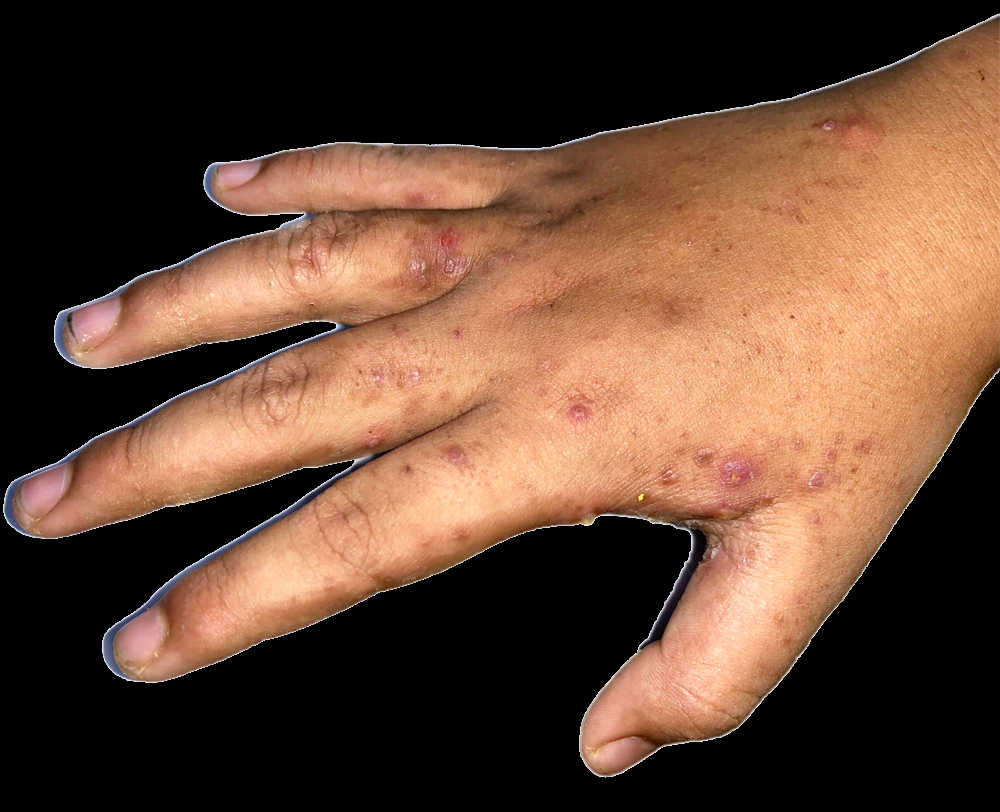
2. Scabies (Sarcoptic Mange)
Scabies is caused by microscopic mites called Sarcoptes scabiei that burrow into the skin. In dogs, this condition is often called sarcoptic mange.
What it looks like in dogs: Intense itching, redness, hair loss, and crusty skin, often starting on the ears, elbows, and stomach.
What it looks like in humans: A red, intensely itchy rash with small bumps and sometimes visible burrow lines where the mites have tunneled under the skin.
How it transfers: Direct contact with an infected dog. These mites love to hang around kennels and pet shops.
Treatment: Prescribed medications for both you and your pet. Your doctor will likely give you a lotion to kill the mites, while your vet will prescribe appropriate treatment for your dog.
I can personally vouch for how miserable this condition is! When I was about 8 years old, my entire family got infected with scabies. The itching was unbearable, especially at night. Our doctor prescribed a special lotion that finally brought relief.
3. Bacterial Infections (including Staph/MRSA)
Yes, the same staph infections you hear about in hospitals can be passed between dogs and humans.
What it looks like in dogs: Red bumps, pimples, or oozing sores, often in areas where the fur is thin.
What it looks like in humans: Red, swollen areas that may develop into painful bumps filled with pus.
How it transfers: Contact with infected skin, or if dog saliva containing the bacteria enters a cut or scrape on your skin.
Treatment: Antibiotics, though some strains (like MRSA) are resistant to common antibiotics and require special treatment.
What’s particularly tricky about staph infections is that dogs often pick up the bacteria from humans first, then pass it back to us in a more dangerous form.
4. Hookworm
While not a rash in the traditional sense, hookworm can cause a skin condition called cutaneous larva migrans or “creeping eruption.”
What it looks like in dogs: Dogs might show signs of anemia, weight loss, or diarrhea, but often show no skin symptoms.
What it looks like in humans: Red, extremely itchy, raised tracks on the skin (usually on feet, legs, or buttocks) where the larvae are migrating under your skin.
How it transfers: Walking barefoot on soil or sand contaminated with infected dog feces.
Treatment: Anti-parasitic medications prescribed by your doctor.
5. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Though technically not a rash that originates from dogs, they can bring the ticks that cause this serious illness into your home.
What it looks like in dogs: Fever, joint pain, and sometimes a spotted rash on the skin.
What it looks like in humans: Fever, headache, and a distinctive spotted rash that typically starts on wrists and ankles.
How it transfers: Through the bite of an infected tick that may have hitched a ride on your dog.
Treatment: Antibiotics, which should be started as soon as possible.
How to Protect Yourself While Loving Your Dog
Don’t worry – you don’t need to stop cuddling your furry friend! Here are some practical steps to reduce your risk:
Regular Vet Care
The single best way to prevent zoonotic skin problems is to ensure your dog has regular veterinary checkups. If you notice any skin changes, unusual scratching, or hair loss, get them checked right away.
I know vet bills can add up fast. If money is tight, look into:
- Low-cost community clinics
- Animal shelter veterinary services
- Payment plans at your regular vet
- Care Credit (a credit service specifically for medical and veterinary expenses)
Good Hygiene Practices
Some simple habits can make a big difference:
- Wash your hands thoroughly after petting or playing with your dog
- Don’t let your dog lick your face or any cuts/scrapes on your skin
- Regularly wash your dog’s bedding and toys
- Consider keeping your dog off furniture and beds if they’re showing any signs of skin problems
- Bathe and groom your dog regularly (but not too frequently, as over-bathing can cause skin issues)
Parasite Prevention
Many skin problems start with parasites:
- Keep your dog on year-round flea and tick prevention
- Use monthly heartworm prevention that also controls intestinal parasites
- Clean up dog poop promptly from your yard
- Don’t let your dog drink from standing water or ponds
Watch for Warning Signs
Early intervention is key! Be on the lookout for:
- Excessive scratching, licking, or biting at the skin
- Red, irritated skin
- Hair loss or thinning fur
- Any unusual bumps, scabs, or sores
- Foul odor from skin or ears
- Shaking the head frequently (can indicate ear issues)
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you develop any unusual rash or skin condition after your dog has been showing skin problems, it’s worth getting checked out. Seek medical attention right away if you notice:
- A rapidly spreading rash
- A rash accompanied by fever
- Severe itching that interferes with sleep
- Any rash that appears to have tracks or seems to be moving
- Painful, warm, or swollen skin
- Any skin infection that doesn’t improve within a few days
Real Talk: My Personal Experience
I’ll never forget the summer our family got scabies. It started with my sister complaining about itching, then within days, all five of us were scratching like crazy. The itching was always worse at night, and I remember my mom checking us with a flashlight after we’d gone to bed, trying to see what was causing the problem.
Our doctor finally diagnosed scabies and explained we’d probably picked it up from our dog. We had to treat not just ourselves but our pup too, plus wash EVERYTHING in hot water. It was a miserable few weeks, but it taught me firsthand how easily skin conditions can pass between pets and people.
A friend of mine had a similar experience when she rescued a dog that turned out to have both scabies AND Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. She ended up with scabies herself before they got the dog proper treatment.
Common Questions About Dog Rashes and Humans
Can I get a skin infection from my dog if they don’t have symptoms?
Yes! Dogs can be carriers of certain bacteria, fungi, or parasites without showing symptoms themselves. They can bring these organisms into your home where they might transfer to you.
Are certain dog breeds more likely to have skin conditions that can transfer to humans?
No, any dog breed can potentially carry transmissible skin conditions. However, dogs with compromised immune systems or those in shelters/kennels are at higher risk of picking up contagious skin problems.
If my dog has allergies, can those transfer to me?
No, allergies themselves aren’t contagious. However, excessive scratching from allergies can lead to secondary skin infections in your dog that could potentially transfer to you.
Can children get skin infections from dogs more easily than adults?
Yes, children are generally more susceptible because they:
- Have closer physical contact with dogs
- May not wash their hands as thoroughly
- Have developing immune systems
- Are more likely to touch their face after petting a dog
If I’m immunocompromised, should I be more careful?
Absolutely. People with weakened immune systems should take extra precautions and consult with both their doctor and veterinarian about specific risks and preventive measures.
The Bottom Line
While the idea of catching a skin condition from your beloved pet might be worrying, remember that with proper care and attention, the risk is relatively low. Regular veterinary care, good hygiene, and prompt attention to any skin problems in either you or your dog will go a long way toward keeping everyone healthy and rash-free.
I’ve had dogs my whole life and have only experienced one transferable skin condition – though it was certainly memorable! The benefits of dog companionship far outweigh these risks, especially when you know what to watch for.
So go ahead and give your furry friend some love – just maybe wash your hands afterward, especially if they’ve been scratching more than usual!
Have you ever experienced a skin condition that transferred between you and your pet? I’d love to hear your stories in the comments below!
How Do Pets Spread Infections?
Also like us, animals carry germs. But illnesses common among house pets — such as distemper, canine parvovirus, and heartworms — cant spread to people.
But some types of bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi that pets can carry can make people sick though a bite or scratch, or if someone has contact with an animals waste, saliva, or dander. Infants, kids younger than 5 years old, pregnant women, and people with weak immune systems have a greater chance of getting sick from these.
Consider the type of pet and the health and age of your kids before you get a pet. For example, children whose immune systems are weak (from HIV, chemotherapy treatment for cancer, or steroid medicines) shouldn’t be around cats and dogs with ringworm infections. Kids with eczema should avoid aquariums. Reptiles and amphibians as pets are not a good idea for families with infants, young children, or an immunocompromised family member.
Dogs and cats can carry infections such as:
- Campylobacter infection: In people, this bacterial infection causes diarrhea, belly pain, and fever.
- Cat scratch disease: Signs of this bacterial infection include swollen and tender lymph nodes, fever, headaches, and tiredness.
- Rabies: This serious illness is rare thanks to widespread immunization of dogs and cats in the United States.
- Diseases carried by ticks: Tick-borne diseases can happen when ticks attach to pets outdoors. Use tick prevention products on pets and safely remove and dispose of ticks as soon as possible.
- Ringworm: Kids can get ringworm from touching infected dogs and cats. This can cause a dry, scaly round area with a raised red bumpy border and a clear center.
- Toxocariasis: The eggs of a parasitic roundworm in the intestines of dogs and cats can pass from their poop into soil where kids play. An infected child can have a fever, cough or wheezing, enlarged liver, rash, or swollen lymph nodes.
- Toxoplasmosis: An infection from a parasite found in cat poop usually causes no symptoms in healthy people but can cause serious problems for pregnant women and their unborn babies. So pregnant women and people with weak immune systems should not clean litter boxes.
Pet birds, even if they are kept in a cage, can spread these diseases:
- Cryptococcosis: A yeast in bird droppings, especially from pigeons, it can cause pneumonia and meningitis in people with weak immune systems, particularly people with HIV/AIDS.
- Psittacosis: A type of bacteria can infect pet birds, and someone who has contact with their poop or the dust that builds up in birdcages can develop psittacosis, also called parrot fever. Symptoms include coughing, high fever, and headache.
Backyard poultry, including chickens and ducks, can also carry harmful germs, including Salmonella. Young children and people with weak immune systems should not touch backyard chickens and other live poultry.
Reptiles (including lizards, snakes, and turtles) and amphibians (including frogs, toads, and salamanders) are not recommended as pets for kids younger than 5 because of salmonellosis. This infection causes symptoms such as belly pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and fever. Young children can get very sick with dehydration, meningitis, and sepsis (blood infection).
Infections from handling and caring for rodents and fish include:
- Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV): People can get LCMV when exposed to pee, poop, or spit from infected rodents. Pet mice, gerbils, hamsters, and guinea pigs usually don’t carry LCMV but can get infected if around wild mice at the breeder, pet store, or in the home. This infection causes flu-like symptoms — fever, tiredness, headaches, muscle aches, nausea, and vomiting — and may lead to meningitis and encephalitis. It can cause serious problems for infected pregnant woman and their babies.
- Mycobacterium marinum: This infection happens when people with breaks in their skin are exposed to contaminated water in aquariums or pools. These infections are generally mild and limited to the skin but can be more serious in people with HIV/AIDS or weak immune systems.
How Can We Safely Care for a Pet?
Here are some tips to help your family safely care for pets:
- After you choose a family pet, take it to a veterinarian for vaccinations and an exam. Schedule regular checkups and routine vaccinations for your pet as recommended. This will keep your pet healthy and lower the chances that it can spread an infection to your family.
- Teach your children to wash their hands after touching pets, handling your pets food, or cleaning your pets cage, tank, or litter box. Wear gloves when cleaning up animal waste. If you have a bird, wear a dust mask over your nose and mouth when cleaning the cage or coop. Dont let kids clean cages or litter boxes until they’re older and know how to do this safely and responsibly.
- Have kids wash their hands after visiting petting zoos, farms, or friends’ houses where there are animals.
- Remind family members to avoid kissing or touching your pet’s mouth because infections can spread through saliva.
- Keep your pets living area clean and free of waste. If your pet goes outdoors, pick up waste regularly and dont let kids play in that area.
- If possible, keep pets out of areas where food is prepared or handled, and dont bathe your pet or clean aquariums in the kitchen sink or bathtub. Wash your pet outdoors or consider professional pet grooming.
- Avoid strange animals or those that look sick. Never adopt a wild animal as a pet.
- Watch kids carefully around pets. Young kids are more likely to catch infections from pets because they crawl around on the floor with the animals, kiss them or share food with them, and put their fingers and things in their mouths that may be contaminated.
Talk to your doctor if you have questions about infections from pets. If you have concerns about your pet’s health, talk to your veterinarian.
